Overview
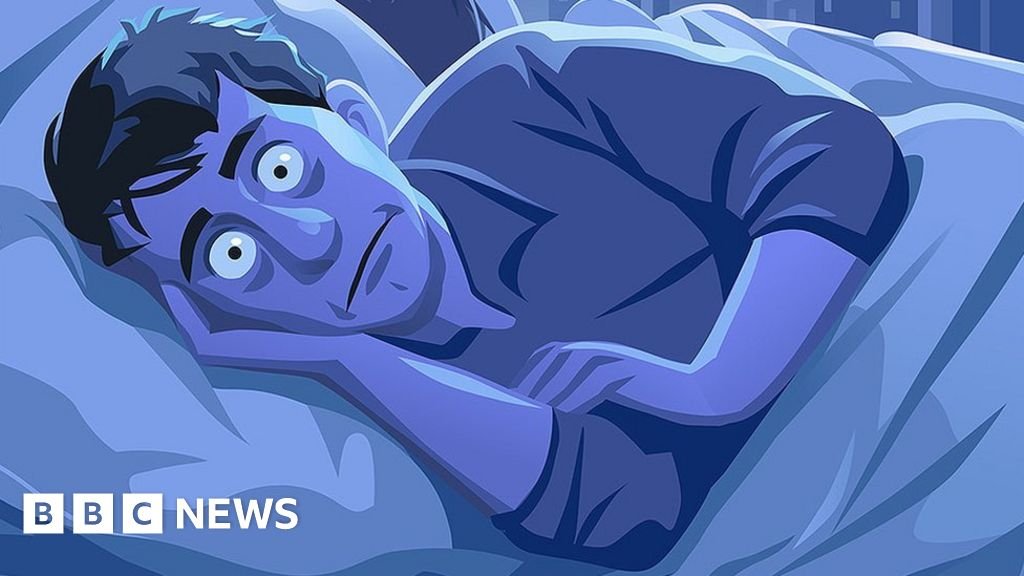
With sleeplessness being one of the most common sleep disorders in our fast-paced environment, sleep problems have become more widespread. The inability to fall or stay asleep, or insomnia, can have a significant impact on a person’s general health. Although the effects of insomnia on mood and day-to-day functioning are well known, its effects on heart health are not as well known. Insomnia and cardiovascular health are closely related, and this article explores how persistent sleep disorders can raise the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems.The relationship between heart health and sleeplessness emphasizes how crucial it is to treat sleep disturbances as part of an all-encompassing strategy for cardiovascular wellbeing.
Modifications insomnia:
In addition to having a negative impact on mood and day-to-day functioning, chronic insomnia raises serious risks to heart health due to metabolic disturbance, elevated sympathetic nervous system activity, inflammation, and changes in hormone levels. Better sleep hygiene, counseling, medication, and lifestyle modifications can all help reduce the dangers associated with insomnia and support heart health. People can take proactive measures to improve their heart health and sleep quality by acknowledging and addressing the reciprocal relationship between sleep and cardiovascular health
Comprehending Sleeplessness
Having trouble falling or staying asleep, or getting up too early and being unable to go back to sleep, are symptoms of insomnia. It may be chronic, continuing for months or even years, or acute, lasting only a short while. Cardiovascular disease is one of the many health issues that chronic sleeplessness is frequently associated to.
Mechanisms Connecting Heart Health and Insomnia
Elevated Sympathetic Nervous System Activity:
Increased exercise like this can lead to the development of cardiovascular problems like hypertension.
Inflammation:
When someone has insomnia, their levels of inflammatory indicators, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), are higher. One known risk factor for atherosclerosis, or the accumulation of fatty deposits in the arteries, which can result in heart disease, is chronic inflammation.
Metabolic Disruption:
Sleep deprivation frequently causes disturbances in metabolic functions, such as fat metabolism. Individuals who have heart disease are more likely to experience recurrent breathing disruptions during sleep, which is the hallmark of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep apnea can accelerate the development of heart disease and aggravate cardiovascular issues.
Modified Hormone Levels:
Lack of sleep has an impact on the control of hormones like cortisol and leptin, which are vital for heart health. Poor sleep raises cortisol levels, which raise blood pressure and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Risks to the Heart Associated with Sleeplessness
There are various ways that sleeplessness might affect cardiovascular health:
Hypertension:
Research indicates that those who have persistent sleeplessness are more likely to acquire hypertension. Prolonged hypertension can harm blood arteries and raise the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Coronary Artery Disease:
People who suffer from sleeplessness can have more plaque accumulation in their coronary arteries, which would decrease the amount of blood going to their heart muscle.
Heart Failure:
Heart failure may occur as a result of the burden that long-term sleeplessness and illnesses like diabetes and hypertension place on the heart.
The Mutually Informed Partnership
There is a reciprocal association between heart health and sleeplessness. As an illustration:
Individuals who have heart disease are more likely to experience recurrent breathing disruptions during sleep, which is the hallmark of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep apnea can accelerate the development of heart disease and aggravate cardiovascular issues.
Stress and Anxiety:
This leads to a vicious cycle in which lack of sleep makes cardiovascular issues worse, and cardiovascular issues make lack of sleep worse.
Control and Avoidance
An interdisciplinary approach is necessary to address insomnia and its effects on heart health:
Enhancing one’s sleep hygiene can aid in the management of insomnia. This entails sticking to a regular sleep schedule, setting up a cozy sleeping space, and abstaining from stimulants like caffeine and nicotine right before bed.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Sleep apnea can accelerate the development of heart disease and aggravate cardiovascular issues.
Cardiovascular Risk Factor Identification and Management:
Monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol, and glucose levels on a regular basis can assist in identifying and managing cardiovascular risk factors. Reducing the risk of heart disease linked to sleeplessness requires treating diseases like diabetes and hypertension.
In summary
The relationship between heart health and sleeplessness. Emphasizes how crucial it is to treat sleep disturbances as part of an all-encompassing strategy for cardiovascular wellbeing. In addition to having a negative impact on mood and day-to-day functioning. Chronic insomnia raises serious risks to heart health due to metabolic disturbance, elevated sympathetic nervous system activity. Inflammation, and changes in hormone levels. Better sleep hygiene, counseling, medication, and lifestyle modifications. All help reduce the dangers associated with insomnia and support heart health. People can take proactive measures to improve their heart health and sleep quality by acknowledging and addressing the reciprocal relationship between sleep and cardiovascular health.


More Stories
Dental Implant Pricing: Expert Guide & Insights
Your Path to Parenthood: Affordable & Transparent Surrogacy
Multivitamins for Women’s Stress Relief