Dental Bone Graft:
A dental bone graft is a surgical procedure used to replace or augment bone in the jaw, often required when a patient has experienced bone loss. Bone grafting is commonly used in preparation for dental implants, as a stable and healthy jawbone is crucial for successful implant placement. This article will explain the dental bone graft procedure, its importance in dental health, and what patients can expect during and after the treatment.
What Is a Dental Bone Graft?
A dental bone graft involves taking bone material from a patient’s own body, a donor source, or a synthetic material and placing it in areas of the jaw that have deteriorated. Over time, the graft encourages new bone growth, strengthening and stabilizing the jaw. Bone loss in the jaw can occur due to several reasons, including:
- Tooth loss: When a tooth is missing for an extended period, the surrounding bone begins to resorb, or shrink, due to a lack of stimulation.
- Periodontal (Gum) disease: Advanced gum disease can damage the bone supporting the teeth, leading to bone loss.
- Trauma or injury: An injury to the mouth or jaw can cause bone deterioration.
- Infections: Severe oral infections can weaken the bone, resulting in a need for grafting.
Types of Dental Bone Grafts
There are different types of bone grafts depending on the source of the grafting material:
- Autograft (Autogenous Bone Graft): This type uses the patient’s own bone, usually taken from another area of the body, such as the chin or hip. Autografts are considered the gold standard because they contain living bone cells that encourage bone growth.
- Allograft: This bone comes from a human donor, typically from a bone bank. The material is thoroughly screened and treated to ensure it is safe and suitable for grafting.
- Xenograft: In this case, the bone material comes from an animal source, most commonly bovine (cow) bone. Like allografts, xenografts are processed to ensure safety.
- Alloplastic Grafts: These use synthetic materials, often made from calcium phosphate or similar substances, to act as a framework for the patient’s bone to grow into.
Each type of bone graft has its advantages, and the choice will depend on the patient’s needs, preferences, and the dentist’s recommendation.
Why Is a Dental Bone Graft Necessary?
Bone grafting is essential in several dental situations, particularly when there has been significant bone loss in the jaw. The most common reasons for dental bone grafting include:
1. Preparation for Dental Implants
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots that are surgically placed into the jaw to hold a replacement tooth or bridge. Implants need a solid foundation, and if a patient has insufficient bone density due to tooth loss or other factors, bone grafting may be required to rebuild the bone before implant placement.
2. Restoring Jawbone Health After Tooth Loss
When a tooth is lost, the jawbone beneath it no longer receives the stimulation it needs to maintain its density and structure. Over time, this bone begins to resorb, or shrink. A bone graft can help rebuild the lost bone and prevent further deterioration.
3. Treating Bone Loss Due to Gum Disease
Advanced periodontal disease can lead to bone loss around the teeth, which can cause them to become loose or even fall out. A bone graft can help restore the bone and save the remaining teeth.
4. Trauma or Injury Recovery
Bone grafts are sometimes necessary following accidents or injuries to the jaw. Trauma can lead to fractures or bone loss, and grafting helps restore the bone structure.
The Dental Bone Grafting Procedure
The dental bone grafting procedure typically takes place in a dental or oral surgery office under local anesthesia, though sedation may be used if needed. Here’s what to expect during the process:
1. Preoperative Consultation
Before the procedure, your dentist or oral surgeon will take X-rays or a CT scan to assess the condition of your jawbone. This allows them to determine the extent of the bone loss and the type of graft required.
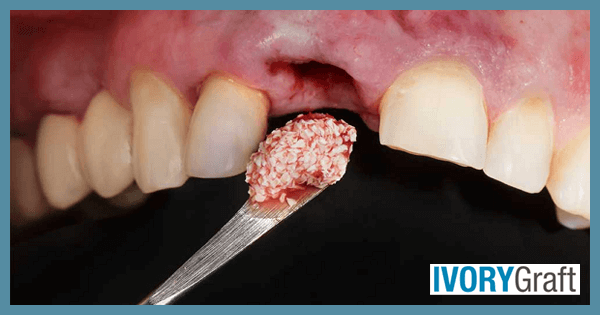
2. Grafting Procedure
Once the area is numb, the dentist will make a small incision in the gum to expose the bone. The graft material is then placed in the area where the bone has deteriorated. In some cases, a membrane is used to protect the graft and encourage proper healing.
3. Healing and Recovery
After the graft is placed, the healing process begins. Over several months, the grafted material integrates with the existing bone, encouraging new bone growth. The success of the procedure depends on careful post-operative care and following your dentist’s instructions. Most patients experience minimal discomfort, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
Aftercare and Recovery
Recovery from a dental bone graft typically involves minimal downtime. Most patients can return to normal activities within a few days. However, proper aftercare is crucial to ensure the graft heals successfully. Post-procedure care includes:
- Avoiding chewing on the grafted area for a period of time to allow for healing.
- Eating soft foods during the initial days following the surgery.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene, but being cautious around the grafted area to avoid disturbing the graft.
- Following up with the dentist to monitor healing progress and ensure the graft is integrating properly.
Possible Complications
While dental bone grafting is generally a safe and successful procedure, there are some risks involved, including:
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a small risk of infection.
- Graft failure: In some cases, the graft may not integrate with the existing bone, requiring further treatment.
- Inflammation or pain: Swelling or discomfort is common but usually subsides within a few days.
Your dentist will discuss these risks with you before the procedure and take steps to minimize them.
The Importance of Dental Bone Grafting for Long-Term Oral Health
Dental bone grafting plays a critical role in maintaining and restoring the structure of the jawbone. Without sufficient bone density, patients may not be candidates for dental implants, and they may experience additional tooth loss or jawbone deterioration. Bone grafting helps preserve the natural contours of the face and mouth, ensuring long-term oral health and stability.
Conclusion
A dental bone graft is a valuable procedure for individuals experiencing bone loss in the jaw due to tooth loss, gum disease, or trauma. It is often essential for preparing the jaw for dental implants and restoring overall oral health. If you’ve been told you need a bone graft, rest assured that the procedure is safe, effective, and can significantly improve your dental outcomes. As always, consult with your dentist or oral surgeon to determine the best approach for your specific situation and ensure a successful recovery.

More Stories
Dental Implant Pricing: Expert Guide & Insights
Your Path to Parenthood: Affordable & Transparent Surrogacy
Site Oficial Para Cassino Online E Apostas No Brasil