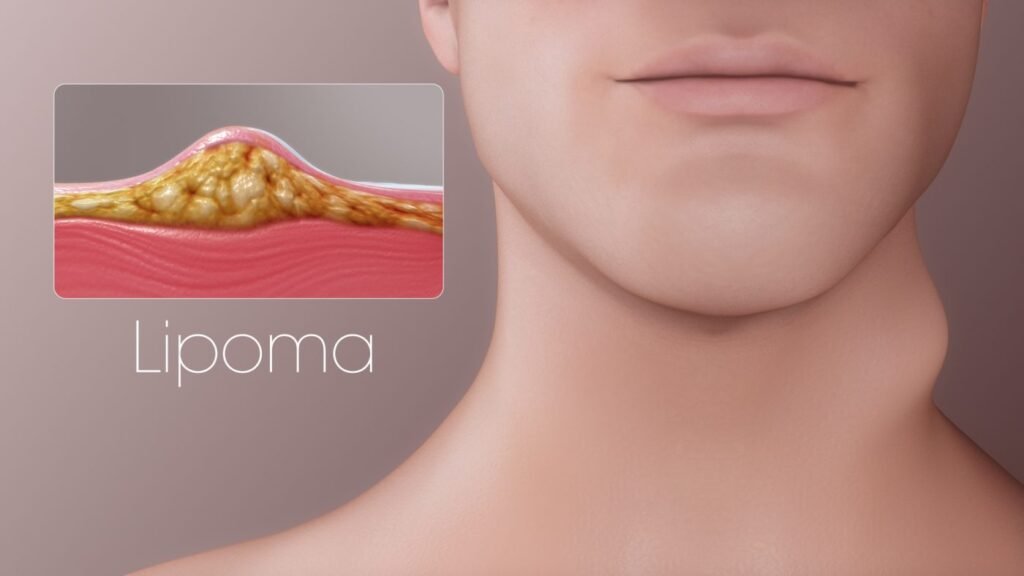
Lipomas are common, benign growths of fatty tissue that appear just beneath the skin. Though typically harmless, they can be concerning if you’ve never encountered one before. Let’s explore the facts of lipomas and the type of benign soft tissue tumor. Understand their characteristics and risk factors. Learn about Lipomas diagnostic methods and find available treatments for managing these harmless growths.
What Are Lipomas?
Lipomas comprise fat tissue and non-cancerous tumors ranging from less than an inch to many inches in diameter. They are soft tissue tumors that typically grow beneath the skin. They are more effective in men than women and are generally found in adults. These are usually slow-growing and can arise anywhere where fat cells are present. Lipomas are not painful and do not cause a serious health risk. Most Lipomas are not painful. They are mostly found in the neck, shoulders, back, abdomen, or arms and thighs.
Read more here
Diagnosis of Lipomas
Diagnosing a lipoma includes a mixture of a physical examination and imaging tests. Here are some steps includes:
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will observe the lump by noticing its size and texture. Lipomas can usually easily move under the skin. They are not painful unless they press on nerves. In addition to these observations, a doctor might feel the area around the lump to see if there are any attached tissues.
Medical History
The doctor may discuss the patient’s medical history, involving any family history of lipomas. This can help discover the possibilities of a lipoma versus other types of growth. Knowing if the patient has experienced any recent injuries or insect bites in the area can also be helpful for diagnosis.
Imaging test
Imaging tests can provide more detailed information, but a physical examination is enough to diagnose a lipoma.By the use of Ultrasound, go through the first imagining test. This non-intrusive test uses sound waves to create images of the lump and can help differentiate a lipoma from other soft tissue tumors. Magnetic Resonance Imaging can provide more detailed photos, which is especially useful for deep lipomas.
Biopsy
A biopsy may be performed if the lump has uncommon characteristics to confirm the diagnosis. This includes taking a small tissue sample from the suspected lipoma for laboratory analysis. This sample is examined to determine the cells’ nature and confirm the diagnosis.
FAQs about Lipomas and Their Diagnosis
What are lipomas?
Lipomas are benign tumors composed of fatty tissue. They typically develop just beneath the skin and are soft to the touch. Lipomas are usually painless and can occur anywhere on the body where fat cells are present, most commonly on the neck, shoulders, back, abdomen, arms, and thighs. These growths are generally slow-growing and are not cancerous, meaning they do not spread to other parts of the body.
How are lipomas diagnosed?
Lipomas are typically diagnosed through a physical examination by a healthcare provider. During the examination, the doctor will check the texture, size, and mobility of the lump. In most cases, lipomas are easily identified due to their characteristic soft, rubbery feel and ability to move slightly under the skin when pressed.
Do I need any tests to confirm a lipoma diagnosis?
In most cases, no additional tests are required to diagnose a lipoma. However, if there is any uncertainty about the diagnosis, or if the lipoma is unusually large, painful, or growing rapidly, your doctor may recommend imaging tests such as an ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan. These tests can help differentiate a lipoma from other types of growths or conditions. In rare cases, a biopsy might be performed to rule out cancer.
What are the symptoms of a lipoma?
Lipomas are usually asymptomatic, meaning they do not cause symptoms. However, they may become noticeable due to their physical presence. The most common symptoms include:
- A soft, doughy lump under the skin
- The lump is usually movable and painless
- Slow growth over time
In some cases, if a lipoma presses on nerves or blood vessels, it might cause pain or discomfort.
When should I see a doctor about a lipoma?
You should see a doctor if you notice any of the following:
- A lump that is growing quickly
- A lump that is painful or tender
- A lump that feels hard or immovable
- Any changes in the skin over the lump, such as redness or warmth
- Concerns about the cosmetic appearance of the lump
Can lipomas turn into cancer?
Lipomas are benign tumors and do not turn into cancer. However, it is important to monitor any changes in the lump and consult with a healthcare provider if you notice any unusual changes or symptoms. This is why it is essential to seek medical advice for any suspicious or rapidly growing lumps.
Are there any risks or complications associated with lipoma removal?
Lipoma removal is generally a safe procedure, but as with any surgery, there are potential risks and complications. These may include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Scarring
- Recurrence of the lipoma
It is important to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider before undergoing any treatment.
Rejuvenate Clinic: Trusted Partner for Lipoma Removal London
Understanding the cost, best clinics, characteristics, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options can help make the correct decision about lipoma removal and is also essential for effective management.
Selecting the best clinic for lipoma removal London includes reputation, surgeon experience, and patient satisfaction. Rejuvenate Clinic in London is best for top lipoma removal services and is well known for its safe and effective treatment results. Rejuvenate Clinic offers personalized solutions customized to meet your unique requirements. They prefer your comfort and satisfaction. Discover peace of mind and confidence in your journey to desirable health and appearance with us.

hgh results after 1 month bodybuilding
References:
sytropin hgh reviews (doc.adminforge.de)
dianabol dosage cycle
References:
Valley.md
hgh x2 somatropinne
References:
hgh dosage for anti aging (images.google.com.hk)
hgh fat loss before and after
References:
does hgh affect testosterone levels
what are steroids made of
References:
long term effects of anabolic steroids (https://git.ides.club/)