Introduction
In the competitive world of modern business, efficiency and streamlined operations are crucial for success. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) software have become essential tools for organizations seeking to optimize their processes and manage resources effectively. This blog delves into the intricacies of ERP and HRMS software, exploring their benefits, key features, and future trends. Additionally, it offers insights into where you can share your blog posts to reach a broader audience.
1. Understanding ERP Software
ERP software is designed to integrate various business processes into a single cohesive system. It facilitates the seamless flow of information across departments, ensuring that every aspect of the business operates in harmony. By consolidating data from areas such as finance, inventory, procurement, and sales, ERP systems provide a comprehensive view of the organization’s performance.
The primary goal of ERP software is to improve efficiency and decision-making. With real-time data access and analytics, businesses can identify bottlenecks, forecast demand, and manage resources more effectively. Modern ERP systems also incorporate AI and machine learning to enhance predictive capabilities and automate routine tasks, further boosting productivity.
2. Benefits of Implementing ERP Software
One of the most significant advantages of ERP software is the improved productivity it brings. By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining workflows, employees can focus on more strategic activities. This leads to faster response times, reduced errors, and increased overall efficiency.
Moreover, ERP systems offer enhanced data security and compliance. With centralized data storage and robust access controls, sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access. Additionally, ERP software ensures compliance with industry regulations by maintaining accurate records and generating necessary reports, reducing the risk of penalties and legal issues.
3. Exploring HRMS Software
HRMS software is designed to manage an organization’s human resources functions efficiently. It covers various HR activities such as recruitment, payroll, benefits administration, performance management, and employee self-service. By automating these processes, HRMS systems free up HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives like talent development and employee engagement.
The integration capabilities of HRMS software are crucial for modern businesses. By linking HR functions with other business processes, such as finance and operations, HRMS ensures that all departments have access to up-to-date employee information. This integration enhances collaboration and decision-making across the organization.
4. Advantages of HRMS Software
HRMS software significantly improves HR efficiency by reducing manual data entry and paperwork. Automated payroll processing ensures accuracy and timeliness, while self-service portals empower employees to manage their information, request leave, and access benefits details independently. This not only reduces the administrative burden on HR but also enhances employee satisfaction.
Another key advantage of HRMS software is its ability to facilitate strategic workforce planning. By providing insights into workforce demographics, skills, and performance, HRMS systems help organizations make informed decisions about talent acquisition, development, and retention. This strategic approach ensures that the organization has the right people in the right roles at the right time.
5. Key Features of ERP Software
When selecting ERP software, businesses should consider several key features to ensure it meets their needs. Scalability is crucial, as the system should grow with the organization and accommodate increasing data volumes and user numbers. Integration capabilities are also vital, as the ERP system must seamlessly connect with existing software and processes.
User-friendliness is another essential feature. An intuitive interface and easy-to-navigate system ensure that employees can quickly adopt and use the software effectively. Customizable reporting tools are also important, as they allow businesses to generate tailored reports that provide valuable insights into their operations.
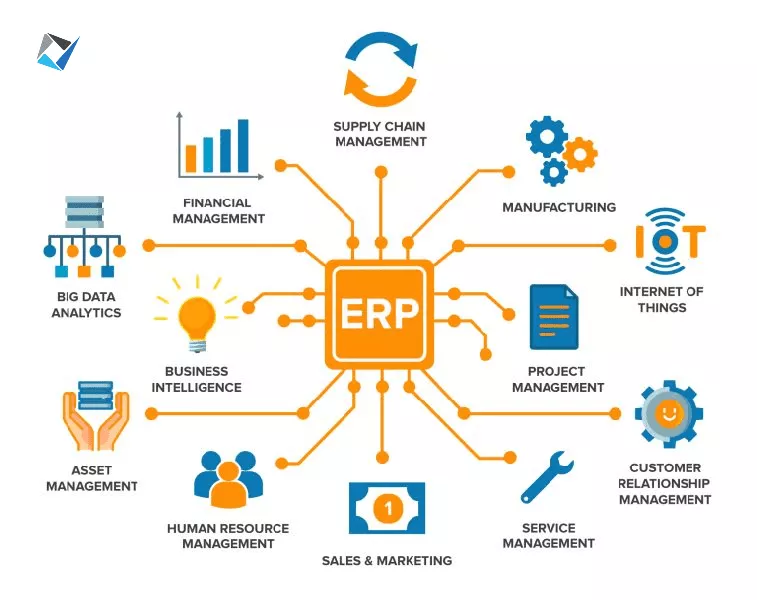
6. Essential Modules of ERP Software
ERP systems typically consist of various modules, each serving a specific function. Financial management modules handle accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting, providing a clear picture of the organization’s financial health. Supply chain management modules oversee procurement, inventory, and logistics, ensuring that goods and services are delivered efficiently.
Manufacturing modules manage production planning, scheduling, and quality control, optimizing manufacturing processes. Customer relationship management (CRM) modules help businesses manage customer interactions, sales, and marketing efforts, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty. Business intelligence modules provide advanced analytics and reporting capabilities, enabling data-driven decision-making.
7. Important Considerations for HRMS Software Selection
When choosing HRMS software, organizations should evaluate its scalability to handle workforce growth and changing HR needs. Compliance with labor laws and regulations is another critical factor, as the system must ensure adherence to legal requirements and industry standards.
Integration capabilities with payroll and other HR systems are essential to ensure seamless data flow and eliminate data silos. Mobile accessibility is also important, as it allows employees to access HR services and information from anywhere, enhancing flexibility and engagement. Additionally, analytics capabilities enable organizations to track HR metrics and performance, supporting strategic decision-making.
8. Trends Shaping ERP and HRMS Software
The ERP and HRMS software landscape is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Cloud-based solutions are becoming increasingly popular due to their flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. They enable organizations to access their systems from anywhere, reducing the need for on-premises infrastructure.
AI and machine learning are also transforming ERP and HRMS software. These technologies enhance predictive analytics, automate routine tasks, and provide personalized user experiences. Mobile applications are another growing trend, offering on-the-go access to critical business functions and improving overall productivity. Enhanced cybersecurity measures are also crucial to protect sensitive data from threats and breaches.
9. Case Studies: Successful Implementation Stories
Many organizations have successfully implemented ERP and HRMS software to achieve significant improvements in efficiency and performance. For instance, a manufacturing company implemented an ERP system to integrate its production, inventory, and sales processes. As a result, they experienced reduced lead times, optimized inventory levels, and increased customer satisfaction.
Similarly, an HRMS implementation at a mid-sized firm transformed their HR operations. By automating payroll and benefits administration, they reduced errors and administrative workload. The self-service portal empowered employees to manage their information, leading to higher engagement and satisfaction. These case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits of ERP and HRMS software in real-world scenarios.
10. Tips for Implementing ERP and HRMS Software
Successful implementation of ERP and HRMS software requires careful planning and execution. Start by setting clear goals and objectives, ensuring alignment with overall business strategy. Engage stakeholders from different departments to gather requirements and address concerns early in the process.
Investing in training and change management is crucial for smooth adoption. Provide comprehensive training to end-users and support them throughout the transition. Conduct regular assessments to measure the software’s impact and ROI, making adjustments as needed. Maintaining open communication with the software vendor is also important for addressing issues and leveraging ongoing support.
11. Future Outlook: Evolving ERP and HRMS Landscape
The future of ERP and HRMS software is promising, with continuous advancements expected to enhance their capabilities. AI and machine learning will play a more significant role in predictive analytics, helping organizations make proactive decisions. Integration with IoT devices will enable real-time data collection and analysis, further improving operational efficiency.
User experience design will continue to evolve, making ERP and HRMS systems more intuitive and user-friendly. Enhanced mobile applications will provide greater flexibility and accessibility, supporting remote work and on-the-go management. As businesses increasingly rely on data-driven insights, ERP and HRMS software will become indispensable tools for strategic planning and growth.
12. Conclusion
ERP and HRMS software are powerful tools that can transform business operations and HR functions. By integrating processes, automating tasks, and providing real-time insights, these systems enhance efficiency, productivity, and decision-making. Organizations that invest in the right ERP and HRMS solutions tailored to their needs will gain a competitive edge and drive sustainable growth in a rapidly evolving marketplace.


Lagi cari game seru yang bisa kasih cuan? Yuk main Plinkball hadiah uang jutaan langsung dari HP-mu
the rock hgh
References:
wehrle
hgh wirkungseintritt bodybuilding
References:
wehrle
Neben Arzneimitteln und qualitativ hochwertiger Kosmetik finden Sie in unserer Onlineapotheke auch Medikamente für Ihr Haustier in unserer Tierapotheke in großer Auswahl.
Mit diesem Beitrag distanzieren wir uns ausdrücklich, von den hier aufgeführten Präparaten und raten dringend, von der Einnahme illegaler Substanzen ab.
Auch bei kurzfristiger Anwendung können diese
Mittel zu ernsten Gesundheitsschäden führen. In Apotheken oder Drogerien werden Sie vergeblich nach
Dianabol suchen. Ein Kauf ist lediglich im Web möglich, wobei es sich nicht als einfach erweist,
einen seriösen Anbieter auszumachen. Besser ist auf jeden Fall nach einer guten Various
zu suchen, die sich zudem als kostengünstiger erweist.
Sogar bei Fortgeschrittenen, erscheint eine Nutzung von zwischen 15 bis
45 mg pro Tag, als vollkommen ausreichend.
Die Dosierung von HGH (100 IU) sollte individuell angepasst werden, abhängig von den Zielen, dem Körpergewicht und der Erfahrung des Benutzers.
Für Amateur-Bodybuilder wird empfohlen, mit einer niedrigeren Dosierung zu beginnen, etwa 2-4
IU pro Tag. Das HGH (100 IU) von Aquila Prescribed Drugs ist ein hochwertiges Wachstumshormon, das speziell für
Bodybuilder und erfahrene Athleten entwickelt wurde. Es ist ein beliebtes Produkt in der Fitness- und Bodybuilding-Community aufgrund
seiner beeindruckenden Vorteile und Wirksamkeit.
Sind Sie privatversichert, können Sie je nach Tarif eine Erstattung
bei Ihrer Versicherung anfragen.
Die Übersäuerung des Muskels wird so verhindert und sorgt für mehr Kraft beim Training.
Unter den beliebtesten Zusatzstoffen findet sich vor allem
Creatin Monohydrat(6). Der Körper kann Creatin zwar selber produzieren, allerdings nur etwa 1 bis
2 Gramm täglich. Für sämtliche Körperfunktionen ist diese Ration in der Regel ausreichend,
kommt jedoch Kraftsport hinzu, müssen Sportler Creatin extra zuführen. Durch
die zusätzliche Einnahme von HGH X2 wird gewährleistet, dass Muskeln schneller aufgebaut werden und die
Regenerationsphase kürzer ausfällt. Sogar die häufig auftretenden Schmerzen in den Gelenken werden von denen, die HGH X2 eingenommen haben, nach einer mehrwöchigen Nutzung,
als Schnee von gestern bezeichnet.
Und weil immer mehr Menschen auf Ihre Kind achten, bieten immer mehr Hersteller Produkte für eine ausreichende
Versorgung des Körpers an. Mit Krafttraining allein ist es nicht getan, denn mangelt es
dem Körper an wichtigen Makro-, als auch an Mikronährstoffen, fehlen den Muskeln wichtige Wirkstoffe für ein perfektes Wachstum, um wirklichen Trainingserfolg zu sehen. Einige helfen jedoch beim Muskelaufbau
nach, und nehmen sogenannten Muskelaufbaupräparate ein, welche in einigen Fällen, als legale Präparate zur Verfügung stehen und auch gegen eine Einnahme, ist letzten endes
nichts negatives einzuwenden. Natürlich hilft ein intensives Training und regelmäßiges Coaching
dem menschlichen Körper immer, wenn mehr Muckis aufgebaut werden sollen und ganz nebenbei entwickelt sich noch mehr Energie.
Viele Männer lieben an ihrem Körper Muskelmasse, aber bitte an an den richtigen Stellen. Sie gehen aus diesem Grund,
wenn möglich, mehrere Male in der Woche in ein Fitnessstudio um den Muskelaufbau voranzutreiben. Die besten Muskelaufbaupräparate 2025 sind TestoPrime, D-Bal, Trenorol, Anadrole und HGH-X2,
die wir nach umfangreichen Tests als Top-Auswahl
für maximalen Muskelaufbau identifiziert haben.
HGH X2 ist das Nahrungsergänzungsmittel, für all diejenigen, die trotz einem intensiven Training keine Muskeln ansetzen oder nicht
die erwünschte Masse an Muskeln erreichen. In der Regel wird HGH vom Körper durch
die körpereigene Hypophyse selber produziert, dieses lässt jedoch mit
Zunahme des Alters ab. Das Produkt zeichnet sich weiterhin dadurch
aus, dass es keine verbotenen Substanzen enthält, sondern nur aus pflanzlichen und
somit natürlichen Inhaltsstoffen hergestellt wurde und aus diesem
Grund, bestens für eine Vitamin ist.
Durch die Riesenauswahl an Arzneimitteln und Apothekenkosmetik zu besonders kleinen Preisen, ermöglichen wir Ihnen eine schnelle
und komfortable Bestellung für Sie und Ihre ganze Familie.
Bei uns können Sie schnell, und vor allen Dingen günstig, Ihre Medikamente bestellen. Die strukturierte Navigation unserer Internetapotheke
erleichtert Ihnen die Suche Ihres Produktes. Geben Sie dazu einfach den Namen oder die Marke Ihres gewünschten Produktes in die Suchleiste ein oder nutzen Sie die thematisch geordneten Kategorien.
Da diese legal sind, unterliegen Sie nicht der ethischen Belastung der
Illegalität. Vor allem aber sollten Sie sich gesund ernähren und Sport treiben, um in Type zu bleiben. Auch sehr wichtigist
die Ernährung – essen Sie Speisen, die aus mehr Protein und wenigerKohlenhydraten bestehen,
denn es ist bewährt, dass die Aminosäuren, die sich improteinreichen Lebensmittel befindet, das Niveau der Wachstumshormone steigert.
Wachstumshormone, die man noch HGH nennt, sind die Hormone, die
sehr stark sind und die für denMuskelaufbau verantwortlich sind.
HGH ist noch stärker als Testosteron Produkte, denn es ist dasMasterhormon im
unseren Organismus und es kontrolliert alle
Wachstumsprozesse.
Für Amateur-Bodybuilder wird empfohlen, mit einer niedrigeren Dosierung zu beginnen, etwa 2-4 I.E.
(Internationale Einheiten) pro Tag. Erfahrene Athleten können ihre Dosierung auf 4-6 I.E.
erhöhen, um maximale Ergebnisse zu erzielen. Bisher wurde das Produkt HGH-X2 weder
von der Stiftung Warentest noch von der Verbraucherzentrale oder anderen Verbraucherschutzorganisationen getestet.
Verbraucher, die sich für dieses Produkt interessieren, sollten daher besonders auf unabhängige Erfahrungsberichte und wissenschaftliche Studien achten, um eine fundierte Kaufentscheidung zu treffen. Es ist wichtig, sich umfassend
zu informieren und mögliche Risiken oder Nebenwirkungen zu berücksichtigen, da offizielle Testergebnisse derzeit nicht vorliegen. Es ist von großer Bedeutung
für die Zellproduktion, das Wachstum und die Stoffwechselprozesse im Körper.
Lassen Sie sich keine Produkte mit intransparenten und möglicherweise unwirksamen Inhaltsstoffen andrehen.
100-IE-Somatropin-Kits sind als Normal bekannt, es gibt jedoch auch viele andere
Variationen der Kit-Größen. Zum Beispiel finden diejenigen,
die HGH kaufen möchten, häufig Kits mit a hundred IE, 200 IE und a hundred and fifty IE sowie andere Mengen, obwohl dies die drei häufigsten Arten sind.
Auch BCAA sowie Vitamine und Mineralien wie Vitamin D, Vitamin C
und Zink sind für das Bodybuilding ohne Anabolika unerlässlich und können zu mehr Muskelmasse beitragen.
Wir garantieren hohe Qualität von diesem Produkt, denn er, wie alles in der Kategorie Produkte aus der Apotheke, ist direkt aus der
Apotheke gekauft. Man muss klar sein, dass die Wachstumshormone keine magische
Wirkung haben. Wenn Sie HGH in Ihrer Kur verwenden,
gewinnen sie nicht 50 % von neuen Muskeln, wie manche Menschen sagen,
sondern etwa 15 % – das ist aber auch ein gutes und sichtbares Ergebnis.
Vieleprofessionellen Bodybuilder kombinieren HGH mit Testosteron um bessereErgebnisse
beim Muskelaufbau zu erreichen.
References:
bbs.yhmoli.com
hgh bivirkninger
References:
hgh dosage for muscle gain (https://xgo.vn/kristinephilp6)
dbol steroid side effects
References:
2ahukewjkv_v5usvnahvlip4khu09akmq420oa3oecakqcq|the best steroids for muscle growth (https://doodleordie.com/profile/formatthumb4)
buy winstrol online usa
References:
muscle steroids For Sale – https://git.avclick.ru/dexterbeliveau,